- May 23, 2023
- Shruti Garg
- Microbiome, Nutrition, Diet and Supplements
The Gut Feeling: Unlocking the Secrets to Optimal Health
In recent years, gut health has emerged as a hot topic in the world of wellness, and for good reason. Our gut, often referred to as our "second brain," plays a pivotal role in our health and well-being. From digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and mental health, the gut is a complex ecosystem that deserves our attention. In this blog, we'll delve into the importance of gut health and provide practical tips for nurturing a healthy gut.
The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microscopic inhabitants, include bacteria, fungi, and viruses which work in harmony to perform essential functions that impact our physical and mental health. A balanced gut microbiome is crucial for optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system function. It also influences our mood, cognitive abilities, and even our weight.
So, what happens when our gut health is compromised? An imbalance in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can lead to a host of issues, such as digestive problems, weakened immunity, and chronic inflammation. Research has also linked poor gut health to mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression, as well as chronic conditions like obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases.
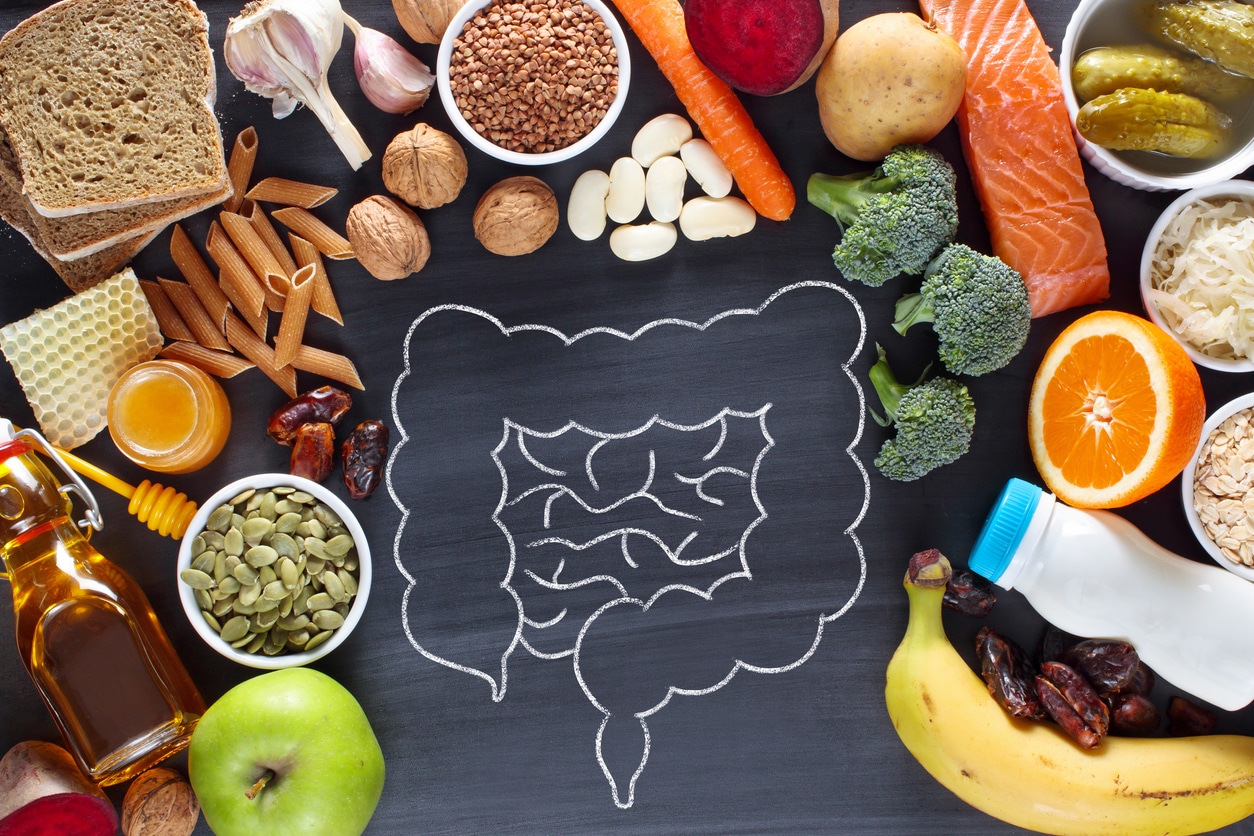

Now that we understand the significance of gut health, let's explore some practical ways to nurture a healthy gut:
- Eat a diverse, fibre-rich diet: A varied diet rich in fibre is essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. Incorporate a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds into your meals. These foods provide the necessary nutrients and prebiotics that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Include probiotics and fermented foods: Probiotics are live microorganisms that can help restore balance in the gut microbiome. You can find them in supplements or naturally occurring in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. Including these foods in your diet can support a healthy gut ecosystem.
- Limit processed foods and added sugars: Processed foods and added sugars can negatively impact gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. Aim to reduce your intake of these foods and opt for whole, unprocessed options whenever possible.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential for maintaining a healthy gut. Adequate hydration helps to promote regular bowel movements and supports the mucosal lining of the intestines, which acts as a barrier against harmful bacteria.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your gut health, leading to an imbalance in the gut microbiota. Incorporate stress-reducing practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine to support a healthy gut.
Gut health is not only about the balance of microorganisms in our digestive system; it also involves the integrity of the gut lining and the efficiency of the gut-brain communication. Let's explore these aspects further:
- Gut lining integrity: The gut lining acts as a barrier between the contents of the gut and the rest of the body. It selectively allows nutrients to pass through while preventing harmful substances and pathogens from entering the bloodstream. A compromised gut lining, often referred to as "leaky gut," can lead to increased intestinal permeability, allowing toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream. This can trigger an immune response, resulting in inflammation and various health issues, such as food sensitivities, skin conditions, and autoimmune disorders. To maintain a healthy gut lining, focus on consuming nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods, and avoid irritants like alcohol, caffeine, and certain medications.
- Gut-brain communication: The gut and brain are in constant communication through the gut-brain axis, a complex network of nerves, hormones, and neurotransmitters. This connection allows the gut to influence our mood, appetite, and stress response. For example, the gut produces around 90% of the body's serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. Disruptions in the gut-brain axis have been linked to mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. To support healthy gut-brain communication, engage in regular physical activity, practice stress management techniques, and consume a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other brain-boosting nutrients.
In conclusion, gut health is a multifaceted concept that encompasses the balance of microorganisms, the integrity of the gut lining, and healthy gut-brain communication. By nurturing a healthy gut through practical tips and focusing on these key aspects, we can optimize our overall well-being and unlock the secrets to optimal health. Remember, a happy gut serves as the foundation for a happier, healthier life. Trust your gut feeling and make prioritizing your gut health an essential part of your daily routine.